Night vision cameras are a testament to our pursuit of enhanced vision in a tech-driven era. These incredible devices have revolutionized our ability to see in the dark. We can now capture images and videos in low-light or dark environments.
Infrared technology is at the center of this transformative capability. It goes beyond what humans can see.
In this article, we will learn about How Infrared Technology Use in Night Vision Camera. They use infrared technology to reveal unseen things in the dark. They give us clear and detailed pictures, even without light.
Contents
Understanding Night Vision Cameras
Night vision cameras are made for use in low light conditions, both indoors and outdoors. These cameras give us a different view than what we see with just our eyes. We can use them for security, watching animals, or in the military.
Taking clear pictures in the dark is difficult because there isn’t much light. Infrared technology helps the camera “see” in the dark.
Introduction to Infrared Technology
Infrared radiation, also called “infrared,” is special in the electromagnetic spectrum. It lies just beyond the range of what our eyes can perceive as visible light. There are two types of wavelengths. One type is short, like ultraviolet and visible light. The other type is long, like microwaves and radio waves. In the middle of this spectrum, there are three main categories of infrared radiation.
- Near Infrared (NIR): This part of the infrared spectrum is similar to visible light. Its wavelengths range from 0.7 to 1.4 micrometers. NIR is often used in remotes, communication, and even medical imaging.
- Mid Infrared (MIR): MIR spans wavelengths from approximately 1.4 to 3 micrometers. It finds applications in areas like spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and some industrial processes.
- Far Infrared (FIR): The FIR region stretches from 3 micrometers to about 1 millimeter. Thermal imaging often uses it to detect temperature differences. It also helps monitor the weather and in some medical applications.
Infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C or -459.67°F). This property makes it incredibly valuable in various applications beyond night vision. To understand night vision technology, we need to know how infrared radiation is used.
How Infrared Technology Use in Night Vision Camera?
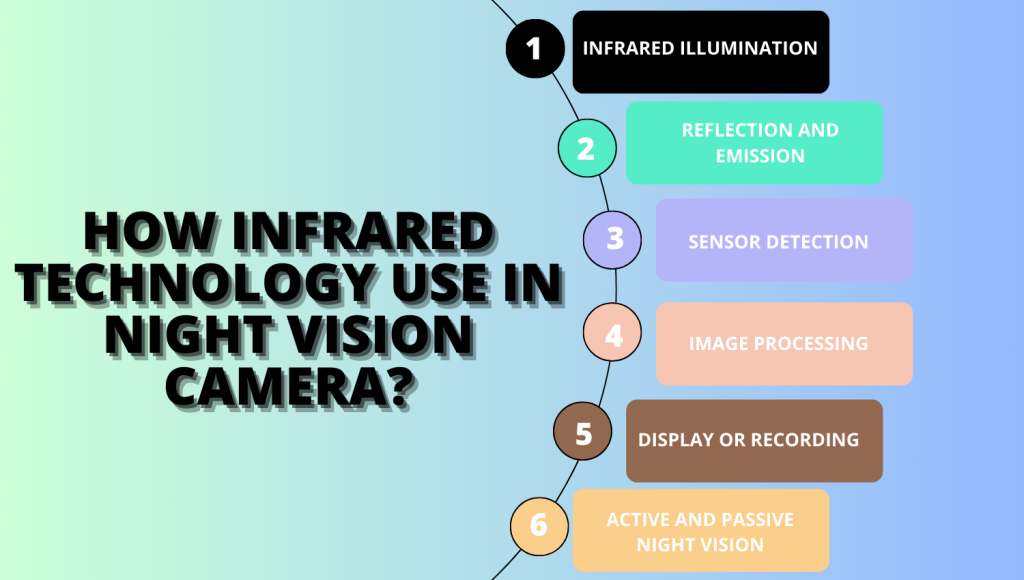
Infrared technology is an integral part of how night vision cameras operate. These cameras can take clear pictures in dark conditions where humans can’t see well. Here’s a breakdown of how infrared technology is used in night vision cameras:
1. Infrared Illumination:
Night vision cameras usually have infrared LEDs built in to provide infrared light. These LEDs emit invisible infrared light, which is beyond the range of human vision. The infrared light makes the scene visible to the camera.
2. Reflection and Emission:
Infrared technology works because objects and living beings emit or reflect infrared radiation. When objects are warmer than absolute zero, they emit heat in the form of infrared radiation. These emissions and reflections occur regardless of whether there is visible light present.
3. Sensor Detection:
Cameras that see in the dark can find and record heat and light that we can’t see. These sensors are often referred to as “infrared sensors” or “IR sensors.” They can sense heat using a specific wavelength and turn it into an electrical signal.
4. Image Processing:
The camera’s internal circuitry processes the captured electrical signals from the IR sensors. This processing involves amplifying the signals and converting them into visible images. The result is an image that shows the scene in real-time, either in black and white or in color.
5. Display or Recording:
The processed images can be displayed in real time on a screen or recorded for later use. You can use night vision cameras with binoculars, goggles, or scopes to see better in the dark.
6. Active and Passive Night Vision:
- Active Night Vision: Some night vision systems operate using active infrared technology. At night, the camera emits its own infrared light to illuminate the scene for clear vision. The camera then captures the reflected light to create images. This method is often used in military and security applications.
- Passive Night Vision: Let you see in the dark using infrared radiation from the moon and stars. Night vision devices for consumers often use systems similar to light amplification.
Infrared technology is crucial for night vision cameras. The device uses a special light to make pictures that we can see. Infrared technology helps us see in the dark. It benefits the military, wildlife, and recreation.
Types of Night Vision Cameras
Night vision cameras have improved a lot thanks to advancements in technology. These cameras are flexible tools. They use different technologies to improve visibility in dark areas. Here, we explore some of the key types of night vision cameras and their specific uses:
01. Image Intensification Night Vision:
- Technology: At night, we use image intensification technology to see in the dark. It amplifies light like moonlight and starlight to make images visible.
- Applications: Military and law enforcement use image intensification night vision. It’s also in civilian devices like night vision goggles and binoculars.
02. Thermal Imaging Cameras:
- Technology: Thermal imaging cameras detect temperature differences in the scene to create images. Objects’ heat is captured and shown as colors or grayscale images.
- Applications: Thermal cameras have many uses. They can find people, fight fires, inspect objects, and study animals. They excel in scenarios where detecting heat variations is critical.
03. Infrared Illuminator Cameras:
Technology: Infrared illuminator cameras flood an area with invisible light using infrared LEDs. This light is then captured by the camera’s sensor and converted into visible images.
Applications: Security systems often use cameras to take clear pictures in dark areas.
04. Active Illumination Night Vision:
Technology: Night vision systems that emit infrared light illuminate the scene effectively. The camera captures the reflected light, creating visible images.
Applications: Active illumination is used in the military and security for long-range surveillance. It is also used in some consumer night vision devices.
05. Digital Night Vision Cameras:
Technology: Digital night vision cameras capture light using sensors and create digital images. They often incorporate image processing algorithms to enhance image quality.
Applications: Various devices like camcorders and hunting binoculars use night vision cameras. They offer the advantage of recording and sharing images and videos.
06. Fusion Night Vision Cameras:
Technology: Fusion night vision cameras use two technologies: image intensification and thermal imaging. This gives a complete view of the scene. These cameras overlay thermal and night vision images for improved situational awareness.
Applications: Fusion night vision is used in high-tech military and law enforcement systems. It helps with identifying things and assessing threats.
To understand night vision cameras, we must know their types and uses in different places. These cameras help us see and work in the dark, whether for military or consumer use.
Limitations and Challenges
Although night vision technology has improved, it still faces challenges and limitations.
Limited Range:
- One of the primary limitations of infrared night vision is its limited range. The range of infrared light changes based on the device’s LEDs or external sources. When it is very dark, the range might be shorter, so it’s hard to see far-away things.
- To overcome this challenge, we need better-infrared illuminators, sensors, and optical components.
Sensitivity to Weather Conditions:
- Weather conditions can significantly impact the performance of infrared night vision. Rain, fog, and heavy snow can scatter and absorb infrared light, reducing visibility. Extreme temperatures can affect how the camera and its infrared parts work.
- Scientists are creating night vision systems that work well in bad weather. They are also developing algorithms that can adapt to different weather conditions.
Cost:
- Night vision equipment, especially for military and professional use, can be expensive. Night vision cameras are expensive because they use advanced technology and precise engineering.
- We are working to make night vision devices cheaper so more people can use them. As technology becomes more commonplace, economies of scale may lead to cost reductions.
Power Consumption:
- Many night vision devices require a considerable amount of power to operate effectively. Portable battery-powered systems often require frequent battery changes or recharging.
- The research wants to make night vision devices last longer. It will do this by making energy-efficient parts and systems.
Resolution and Image Quality:
- Night vision cameras today can take clear pictures, but there is room to make them even better. This is especially crucial in applications where precise identification is essential.
- Scientists are constantly improving night vision systems by enhancing sensors and image processing.
Export Restrictions:
- We cannot sell night vision technology because it is used for the military and security. This can limit the availability of advanced night vision equipment in certain regions.
- Countries are cooperating to find a balance between security and night vision technology.
Despite the challenges, researchers are still improving infrared technology for night vision. As we continue to improve, we get closer to using night vision cameras in new ways.
Future Trends
Night vision cameras with infrared capabilities are ready for significant advancements in technology. In the future, these cameras will be more versatile and accessible. We expect improvements that will make images clearer and more detailed. These advancements are important for precise applications. You can also spot objects and subjects from far away, which helps in important situations.
As technology comes together, artificial intelligence will improve night vision cameras. Machine learning algorithms will make image processing, object recognition, and target tracking better. Advancements in miniaturization will improve portability. Multi-spectral imaging could provide valuable environmental information.
How we use night vision and augmented reality will change how we do tactics and navigation. It will show infrared-enhanced visuals in real time. In the future, night vision will be accessible to everyone and change how we see and move in the dark. It will also be more efficient, and adaptable, and promote global collaboration.
Conclusion
Infrared technology has changed the game for night vision cameras. It lets us see in the dark and capture hidden moments. Better visibility has greatly affected the military, observing wildlife, and products for customers.
As we look ahead, the future of night vision cameras holds tremendous promise. Ongoing research and innovation are helping us make incredible progress in infrared technology. Night vision cameras are improving.
They can capture clearer images and spot objects from farther away. Also they work well with artificial intelligence. They are also using augmented reality technology to change how we see and interact in the dark. The possibilities are growing, making night vision even better and brighter.
Additional Resources
If you want to learn more about infrared photography, here are some extra resources to check out.
- In-depth Night Vision Camera Guide
- Night Vision Camera Product Reviews
- Night Vision Camera Maintenance Tips
Also, Check out our other blog posts about infrared cameras photography, tips and guide!
- Can Any Camera See Infrared Light
- Why is The Infrared On Camera Not Working
- Infrared Light Detection with Camera: Unlocking the Secrets!


